AI Manicure Machines: Transforming Nail Care with Automation & Intelligence
- Technology & Innovation

By
- Updated January 30, 2026
- AI manicure machines merge robotics, 3D scanning, and machine learning to deliver fast, precise, and consistent nail care.
- Two main formats dominate: in-store kiosks (e.g., Clockwork) and at-home devices (e.g., Nimble, Umia).
- Core benefits: speed (10–25 min), cost savings, hygiene, and uniform quality.
- Challenges: limited customization, high initial cost, maintenance, and data/privacy concerns.
- Business impact: salons gain efficiency; retailers attract foot traffic; consumers enjoy convenience.
- Future trends: miniaturized home devices, hybrid human-robot salons, AI-driven design personalization, and better safety standards.
- Bottom line: automation is redefining nail care—turning manicures into a faster, smarter, data-driven experience.
The beauty industry is undergoing a technological revolution, and nail care is no exception. What used to be a manual process—filing, polishing, art design—is beginning to be disrupted by a new wave of AI-driven manicure machines. These devices range from in-store kiosks offering express manicures, to at-home gadgets promising salon-quality nail art with minimal effort. They combine robotics, 3D scanning and deep learning for precision, speed and personalization.
Why it matters:
- Busy consumers increasingly demand convenience without compromising style.
- Salons and retail outlets face staffing & labour cost pressures—automation offers one solution.
- Advances in sensing, computer vision and robotics enable what was once niche R&D to become practical.
- As the nail-care market grows globally, machines that can scale services or reduce labour have potential to reshape the economics of the business.
What are AI Manicure Machines and How Do They Work
At their core, these machines combine several technological elements: robotics (mechanical manipulators, possibly spraying or brushing polish), sensors (3D cameras, LiDAR or structured light), machine vision and deep-learning algorithms (to assess nail geometry, curvature, cuticles, skin vs nail boundary), plus software control and user-interfaces (apps, touch screens).
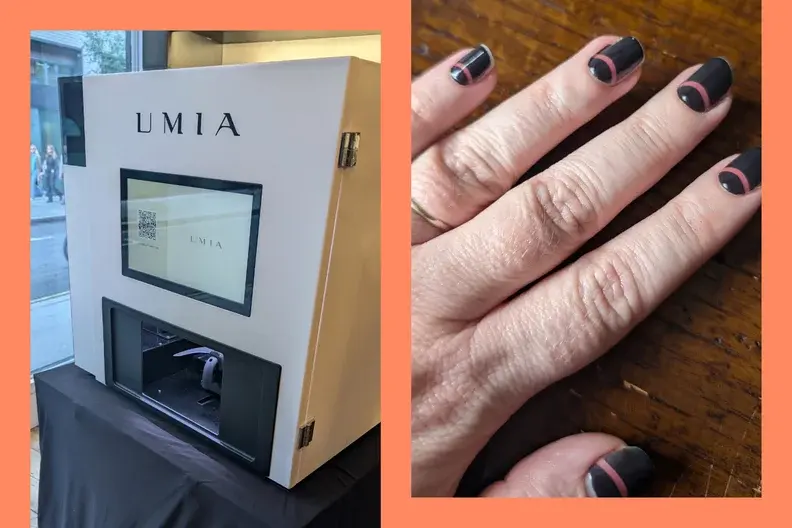
For example, the company Umia uses a convolutional neural network trained on over 120,000 nail-data points to recognise each nail’s width, length and curvature, and distinguish nail plate from skin and cuticle. After each session it collects feedback data and applies an “Adaptive Optimisation Algorithm” to improve alignment and application accuracy.
What does that enable in practice?
- The machine can determine the precise shape of the user’s nail plate and align polish or art design accordingly, reducing mistakes such as spillover onto skin.
- Automated polish application (spray or brush) under robot control yields consistent finish.
- Some systems integrate custom design selection, machine vision-based mapping of the nail’s surface, and even user preference learning (art styles, colours).
- Speed is dramatically faster: some kiosks claim a full manicure in ~10 minutes (much less than many salons). For instance, a service by Clockwork in partnership with Target reported ~10-minute jobs.
In short: it’s not merely a deluxe nail-printer, but a system of sensing + AI + robotics + user interface, designed to automate what was formerly a highly manual, artisan service.
Types and Market Models
1. In-Store / Kiosk Machines
Examples: Clockwork’s “Minicure” kiosk inside Target locations. A consumer books, inserts hand, machine scans nails, applies polish, done in about 10 minutes.
Advantages: High throughput, low labour cost per service, appealing to impulse or convenience-focused customers.
Challenges: Limited service scope (usually one-colour polish, minimal nail prep), user comfort/trust factor, machine maintenance, initial investment cost.
2. At-Home Devices
Companies are emerging that sell devices targeting consumers for home use: simplified scanning + polish application + design.
Benefits: Salon-level finish at home; convenience; appeal to self-care trends.
Limitations: Price, device size/complexity, reliability, user training, selection of designs.
For example, Umia is also aiming at a home-oriented or boutique studio version.
3. Hybrid / Studio Automation Solutions
Nail salons or hospitality environments adopting robot-assisted systems: robot does polish; human does prep/cuticle/care. This allows human technicians to focus on higher-value work (e.g., art, extensions) while robot handles volume tasks. A study indicates that the nail-care industry sees AI + robotics as a strategic partner rather than full replacement of human techs.
Key Features, Benefits & Trade-Offs
Features
- 3D scanning / structured-light or depth-cameras to map nails.
- Machine vision + deep-learning (CNNs) to distinguish nails vs skin/cuticle.
- Robotic arm or automated applicator (spray/brush) with precision algorithms (e.g., identifying nail edge within ±0.3 mm) per research.
- Adaptive learning: system collects data per session, refines model, offers design recommendations.
- UI/UX: App or kiosk touch-screen, design selection, user profile.
- Integration with retail/beauty ecosystems: e.g., in-store kiosks inside retail chains, at-home consumer device ecosystems.
- Analytics & trend forecasting: AI systems can track data (customer colours, shapes) to forecast trends or materials demand.
Benefits
- Speed & throughput: Express service (10–25 minutes) vs typical salon 30–60+ min.
- Consistency & precision: Less dependent on manual technician variability; fewer smudges/spillovers.
- Cost reduction: Lower labour cost, potential higher margin per service, scalability.
- Accessibility: Makes nail-care services accessible in non-traditional venues (retail, airports, at home).
- Data/analytics: Captures usage data for design trends, inventory management, customer preferences.
- Innovation appeal: Technology-savvy consumers like novelty and design variation—robotic machines offer “cool factor”.
Trade-Offs / Challenges
- Limited service scope: Many machines currently offer only polish application, fewer offer full manicure services (filing, cuticle work, extensions). The earlier Clockwork service, for example, did not include full cuticle removal.
- Trust & comfort: Users may feel uneasy that a machine handles their nails; perceiving less “human touch”.
- Initial cost / ROI: Machines require substantial upfront investment (hardware, maintenance); salons must ensure utilization.
- Maintenance & downtime: Robotics and sensors require calibration, cleaning, updates—any breakdowns hurt throughput and brand.
- Cybersecurity & data risk: As machines collect data, and possibly connect to networks, they introduce new vulnerabilities. One research paper highlights cybersecurity risks in nail-care robotics.
- Impact on human jobs: While many systems aim to assist rather than replace, there is concern about automation displacing technician roles; human element remains important.
- Regulation & hygiene: Beauty services have regulatory/hygiene standards; automated machines must meet these (sterility, cleaning, safe polish application).
Business & Market Implications
For Salons & Retail Chains
- Offering “robot manicure kiosks” can differentiate a venue—drawing foot traffic, generating social media buzz (#robotmanicure etc).
- For retail chains (e.g., Target + Clockwork) it allows incremental services inside existing stores, increasing dwell-time and cross-sales.
- Salons can adopt hybrid model: robot for basic polish, human for premium art/extensions—optimising labour.
- Data captured from machines can help forecast demand (colours, designs), optimise stocking of polish, reduce waste.
For At-Home / Consumer Market
- High-end consumers may buy devices for home use, akin to home 3D printers or laser hair removal devices.
- Mainstream adoption will need cost-reduction, compact design, ease-use, robust support.
- Subscription models: device + design library + polish refills + updates.
- Consumer education: ensuring safety, maintenance, cleaning, reliability will matter.
Market Size & Growth
- The nail salon industry globally is large (billions of dollars). A study notes AI and robotics integration in that sector addresses demand for fast/personalised service and labour constraints.
- As machines scale, cost per service could drop, making frequent manicures more accessible.
- Emerging markets (airport lounges, malls, hotels) may deploy kiosks as high-margin convenience services.
- The combination of AI-based analytics (trend forecasting) + automation may open entirely new business models (on-demand nail art vending machines, automated pop-up nail bars).
Emerging Issues & Considerations
Cybersecurity & Data Privacy
As noted in a 2024 paper “Artificial Intelligence and Robotics in the Nail Care Industry”, nail-painting robotic systems are vulnerable to cyber threats—even if public incidents have been rare so far.
Because these machines may store user profiles, design preferences, payment data, and may be network-connected (for software updates, analytics), they become cybersecurity focal points. Salons and vendors must build robust security: encryption, software patching, hardware safeguards.
Human Element & Service Experience
Automation doesn’t fully replace the human touch. Research suggests that although machines can handle volume and consistency, the emotional, aesthetic, and craftsmanship aspects of a human nail technician are still valuable.
There is also a risk of “de-humanisation” of service—if everything is done by machine, will consumers feel less valued or less engaged?
Jobs & Skills
Technician roles may shift rather than vanish: from applying polish manually to supervising machines, doing high-end art, maintaining devices, interpreting analytics. Training and upskilling will matter.
Regulation, Safety & Hygiene
Machines must meet safety standards—no polish overspray, no skin burns, no contamination. Hygiene protocols (e.g., cleaning between users) need to be built in. Machine malfunction could lead to negative customer experience or liability.
Consumer Adoption & Trust
Trust in reliability, quality finish, brand reputation are key. Early users may be tech-savvy; mainstream adoption will require proof of consistent service quality, low-cost, ease-use.
What to Watch: Future Trends
- Improved hardware & mobility: Smaller, cheaper machines for salons and retail; possibly mobile units or vending-style cabinets.
- Advanced customization & design: Machine learning will allow personalised design suggestion (“You liked this style, here’s new palette”), integration with AR (virtual nail preview). Umia already hints at design recommendation via RL.
- Hybrid human-robot service models: Robots handle base tasks; humans handle art/complexity.
- Networked analytics: Aggregated data from many machines across salons/retail will allow trend forecasting (colour palettes, shapes), inventory optimisation for polish manufacturers. (See AI trend-forecasting in nail industry study)
- Expansion into new venues: Airports, hotels, malls, workplaces offering express robot manicures.
- At-home democratization: As cost drops and design libraries grow, home devices may trend similar to robotic vacuums or home-beauty machines.
- Regulatory & standardization frameworks: As automation becomes more common, industry standards for robotic nail care (safety, hygiene, data) will emerge.
- Ethical & job-transition dynamics: How the industry supports technicians transitioning to new roles (supervision, art, machine-maintenance) will matter socially.
China’s humanoid robot ecosystem is rapidly expanding, driven by national strategic priorities and venture capital investment. Leading companies range from established robotics innovators to fast-growing startups. While...
- 01/01/2026
- in Technology & Innovation
China’s Unitree Robotics has begun public beta testing of what it calls the world’s first app store built specifically for humanoid robots. The platform aims to standardize and modularize robot functions, making advanced...
- 23/12/2025
- in Technology & Innovation
Chinese robotics startup TARS has unveiled two new humanoid robot prototypes that highlight its focus on advanced physical intelligence and precision applications such as wire harness assembly and embroidery, tasks that...
- 22/12/2025
- in Technology & Innovation
According to a Reuters investigation dated December 17, China has built and is testing its first domestic prototype of an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machine in a high-security laboratory in Shenzhen. The proto...
- 22/12/2025
- in Technology & Innovation
According to a company press release, iRobot, widely known as the pioneer of robot vacuum cleaners, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the District of Delaware on Decembe...
- 20/12/2025
- in Technology & Innovation
In response to increasingly dynamic manufacturing environments, Chinese intelligent robotics company Huiwen has launched the iBenX series of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to provide flexible, lightweight, and adaptable...
- 12/12/2025
- in Business & Industry
UBTECH Robotics and the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center have jointly established Beijing Tianyou Robotics Co., Ltd., with UBTECH holding a 65% stake and the innovation center holding 35%. The joint venture aims...
- 12/12/2025
- in Technology & Innovation
A research team at Shanghai Jiao Tong University has developed a high-performance electroactive artificial muscle for soft robotics, tactile interaction, and intelligent prosthetics. Their study, recently published onlin...
- 12/12/2025
- in Technology & Innovation